Translate this page into:
Evaluation of Lens culinaris phytochemicals in binding to the 3C-like protease of SARS-CoV-2 – A molecular docking approach

*Corresponding author: Mohammed Rahmatullah, Department of Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering, University of Development Alternative, House 4/4, Block A, Lalmatia, Dhaka - 1207, Bangladesh. rahamatm@hotmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Hasan A, Jahan R, Jannat K, Bondhon TA, Hossan MS, Mazumder S, et al. Evaluation of lens culinaris phytochemicals in binding to the 3C-like protease of SARS-CoV-2 – A molecular docking approach. Indian J Med Sci 2020;72(3):173-6.
Abstract
The novel coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2 and the virus-induced disease COVID-19 has caused widespread concerns due to its contagiousness, fatality rate, and the absence of drug(s). This study investigated Lens culinaris and its phytochemicals, especially the flavonoids. The compounds were assessed through molecular docking studies for their binding abilities with the major protease of the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 (PDB: 6LU7). A total of 42 phytochemicals of Lens culinaris were analyzed through molecular docking studies for their binding affinities to COVID 3C-like protease. Of them, 23 compounds were found to have binding affinities to the protease of −7.5 kcal/mol or higher. Our study indicates that Lens culinaris contains a number of polyphenolic compounds as well as phytosterols, which can bind to the active site of the protease, and so merits further scientific attention on trials for use as potential anti-COVID-19 drugs.
Keywords
SARS-CoV-2
COVID-19
Lens culinaris
Phytochemicals
Bangladesh
INTRODUCTION
The new coronavirus disease known as COVID-19 as of September 27, 2020, has caused 33,092,605 infections and 999,178 deaths worldwide. As of the same date, COVID-19 has infected 7,287,593 persons in the United States of America (USA), which comes to 21,986 cases per million people. In Bangladesh, which has half the population of USA, the situation is better comparatively with 359,148 infections (2176 cases per million people).[1]
It was of interest to look into possible factors for the low rate of infections in Bangladesh. Multiple factors may be involved, one such factor being the diet of the people of Bangladesh, which in its barest essence consists of rice and “daal” (Lens culinaris seed soup).
Our objective was to determine whether phytochemicals present in Lens culinaris could be possible drug targets for SARS-CoV-2. Molecular docking was used to assess if the reported polyphenolic compounds (flavonoids and derivatives) of Lens culinaris could bind to or near the active site of the major protease, 3CLPro, or MPro of SARS-CoV-2 (PDB: 6LU7). We concentrated on polyphenolic compounds (flavonoids and derivatives) since such compounds have been previously implicated in the inhibition of SARS 3C-like protease.[2] The protein with monomeric form was used for the molecular docking model. Phytochemicals present in Lens culinaris were obtained from Ganesan and Xu.[3]
The binding energies (kcal/mol) of various phytochemicals of Lens culinaris are shown in Table. 1. A binding affinity value of −7.5 or more can be considered as possible drug candidates. In fact, atazanavir, fosamprenavir, and lopinavir have been considered approved drugs with anti-viral properties with Autodock Vina binding affinities of −7.2, −7.3, and −7.4, respectively.[4]
For flavanols, catechin gallate, epicatechin gallate, and (+)-catechin-3-O-glucose showed binding affinities of −9.2, −8.3, and −7.6, respectively. Interestingly, in contrast to the flavanols, all the flavonols of Lens culinaris showed binding affinities above −7.5 kcal/mol.
Prodelphinidin (a proanthocyanidin) and eriodictyol-7-O-rutinoside (a flavanone, also known as eriocitrin) showed high binding affinities at −8.5 and −10.1, respectively. Eriodictyol showed a binding affinity of −7.4 kcal/mol, far lesser than eriocitrin [Figures 1 and 2]. Interestingly, it looks like that glycosidic linkages to flavanones significantly enhance the binding affinities to the COVID 3C-like protease, as shown with eriocitrin (versus eriodictyol). The increase of binding affinities with the conjugation of one or more glycosidic moieties holds true also for flavones like luteolin [Table 1].
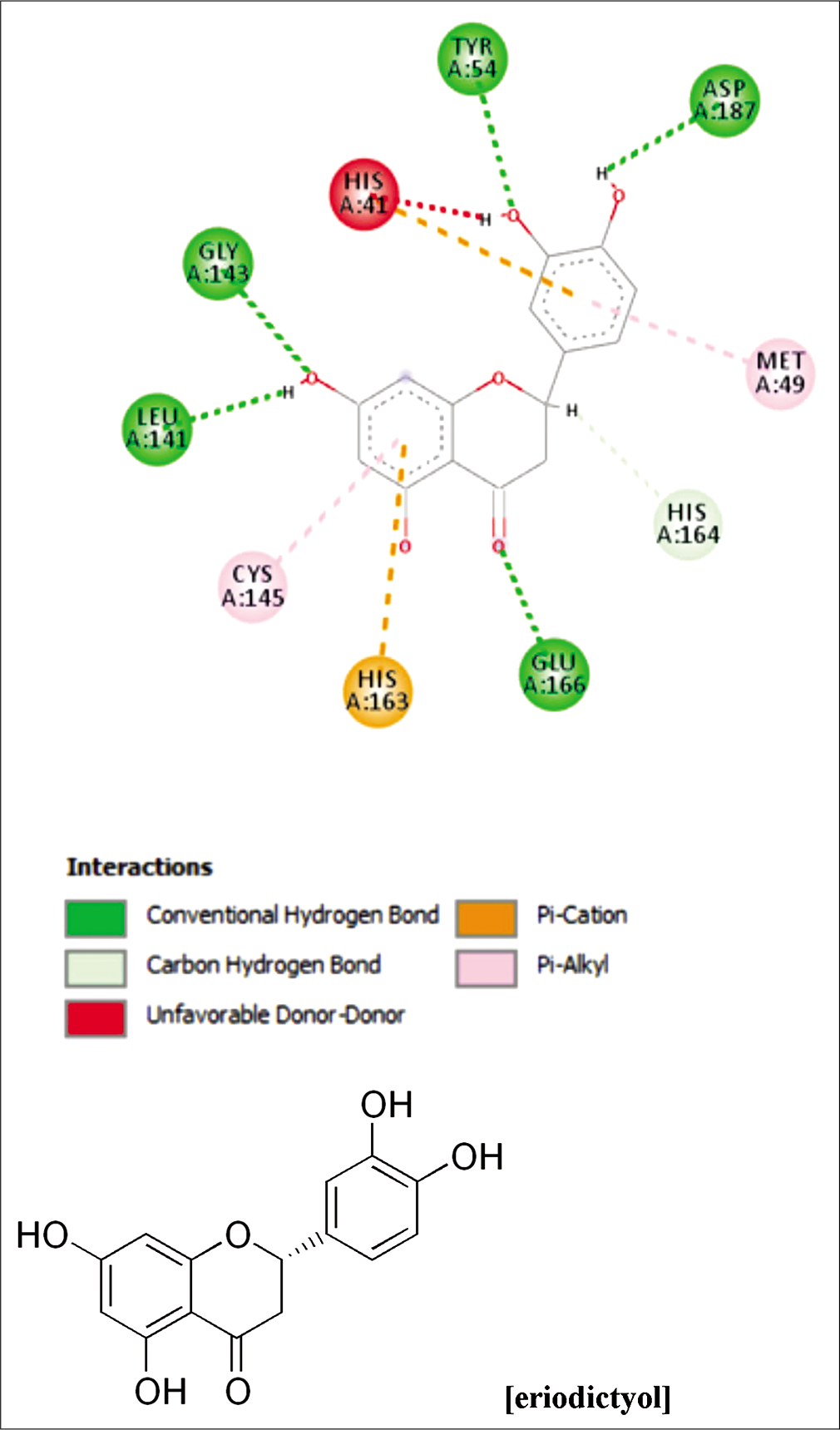
- Building of eriodictyol to SARS-CoV-2-3C-like protease.
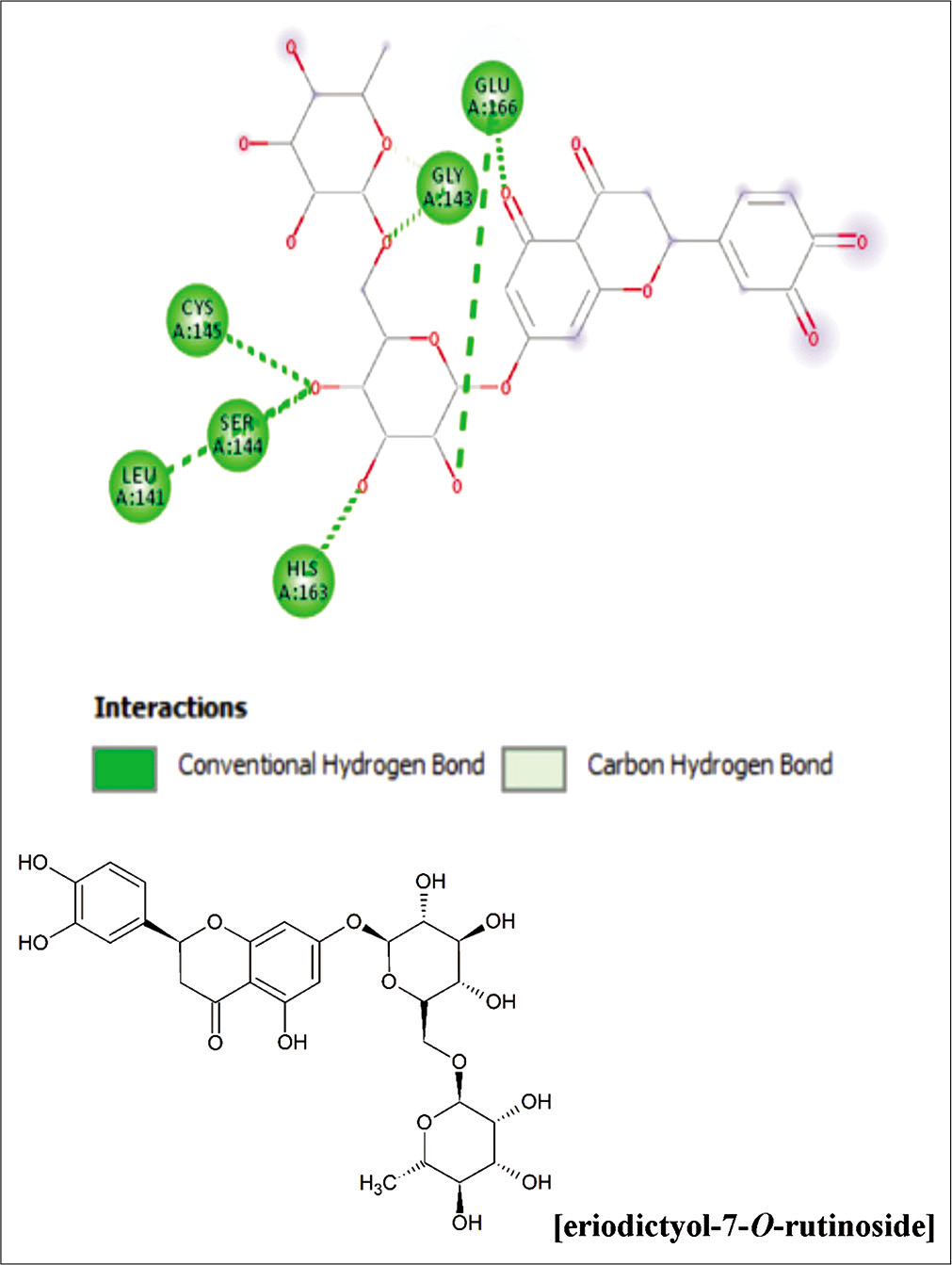
- Building of eriodictyol-7-O-rutinoside to SARS-CoV-2-3C-like protease.
| Phytochemicals | Binding energy (kcal/mol) SARS-CoV-2 | Binding energy (kcal/mol) SARS |
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | ||
| Flavanols | ||
| (-)-Epigallocatechin | −7.2 | −7.2 |
| (+)-Catechin-3-O-glucose | −7.6 | −7.8 |
| Catechin | −7.2 | −7.5 |
| Catechin-7-O-glucoside | −7.3 | −7.5 |
| Catechin gallate | −9.2 | −8.0 |
| Epicatechin | −7.1 | −7.4 |
| Epicatechin gallate | −8.3 | −7.8 |
| Flavonols | ||
| Quercetin-3-O-glucoside | −8.4 | −7.3 |
| Querctin-3-O-galactoside | −8.5 | −7.9 |
| Quercetin-3-O-xyloside | −8.0 | −7.4 |
| Kaempferol-4’-O-glucoside | −7.7 | −7.5 |
| Kaempferol-5-glucoside | −8.3 | −7.4 |
| Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | −8.2 | −7.6 |
| Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside | −8.1 | −7.9 |
| Myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside | −9.0 | −7.3 |
| 4’’’’-Acetylsagittatin A | −7.9 | −8.0 |
| Proanthocyanidins | ||
| Procyanidin | −7.4 | −7.8 |
| Prodelphinidin | −8.5 | −7.3 |
| Flavanones | ||
| Eriodictyol | −7.4 | −7.1 |
| Eriodictyol-7-O-rutinoside | −10.1 | −8.8 |
| Flavones | ||
| Naringenin | −7.7 | −7.2 |
| Apigenin | −7.1 | −7.4 |
| Luteolin | −7.6 | −7.1 |
| Luteolin-4’-O-glucoside | −8.0 | −7.5 |
| Luteolin-3’,7-diglucoside | −8.5 | −8.5 |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucoside | −7.9 | −7.8 |
| 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone | −6.8 | −7.3 |
| Anthocyanins | ||
| Malvidin-3-O-galactoside | −7.7 | −7.7 |
| Non-flavonoids | ||
| Hydroxybenzoic acids | ||
| Syringic acid | −5.4 | −5.4 |
| 2,3-Dihydroxy benzoic acid | −5.5 | −6.0 |
| p-Hydroxy benzoic acid | −5.4 | −5.7 |
| Gallic acid | −5.5 | −6.1 |
| Hydroxycinnamic acids | ||
| 3-Hydroxy cinnamic acid | −5.7 | −6.0 |
| p-Coumaroyl malic acid | −6.1 | −6.7 |
| Sinapic acid | −6.5 | −5.4 |
| Other polyphenols | ||
| 4-Hydroxy-6-methyl coumarin | −6.1 | −6.5 |
| Resveratrol | −6.9 | −6.3 |
| trans-Resveratrol 3-O-b-glucoside | −7.7 | −7.9 |
| Carotenoids | ||
| Lutein | −7.6 | −7.7 |
| Phytosterols | ||
| Stigmasterol | −7.9 | −8.3 |
| Campesterol | −7.5 | −8.2 |
| β-Sitosterol | −7.3 | −8.2 |
We show in this manuscript how consumption of Lens culinaris may contribute to the lower incidences of COVID-19 infections in Bangladesh. To put things in perspective, the population of Bangladesh is 164,363,135, while the population of the USA is 330,626,450 (based on Worldometer elaboration of the latest United Nations data), that is, the population of the USA is basically 2-fold that of Bangladesh. Yet the number of COVID-19 infected cases in the USA is about 20.3-fold more than that of Bangladesh.
It is not claimed that the whole lower infection scenario in Bangladesh is merely an outcome of lentil consumption. Other factors have to be involved, including possible consumption of other dietary items and even possibly environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. However, the lentil contains a large number of phytochemicals (primarily belonging to the flavonoid group of compounds but also phytosterols), which show high binding affinities to the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease. The strong point of the phytochemicals in Lens culinaris is that the lentil is consumed by millions of people every day in Bangladesh; any toxicity would have been noted a long time ago unless the toxicity is neutralized by other phytochemicals.
In a previous molecular docking study conducted with compounds obtained from medicinal plants and the COVID-19 Mpro, a number of flavonoid compounds were postulated as potential inhibitors of the protease.[5] Our study adds significant information to the previous studies in showing that glycosidic derivatives of some flavonoid class compounds show better binding affinities to the protease than the parent compounds. As a result, these flavonoids and their glycosidic derivatives present in Lens culinaris merit scientific attention as potential anti-COVID drugs.
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge the Project CICECO-Aveiro Institute of Materials, UIDB/50011/2020, and UIDP/50011/2020.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- COVID-19 Corona Virus Pandemic. 2020. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus. [Last accessed on 2020 Sep 27]
- [Google Scholar]
- Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3CL protease by flavonoids. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020;35:145-51.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyphenol-rich lentils and their health promoting effects. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2390.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potential Inhibitor of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) from Several Medicinal Plant Compounds by Molecular Docking Study. 2020
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






